What is Human Anatomy?
Human anatomy is a scientific discipline that centers on the detailed study of the structure and organization of the human body. This fascinating field of science delves into the minute details of the body’s structural intricacies, from the minute cells to the vast organ systems, everything falls under its purview.
Key aspects of human anatomy include:
- Cells: These are the smallest and most basic units of life in the human body;
- Tissues: A group of cells working together to perform a specific function forms a tissue;
- Organs: Different tissues, when combined and functioning together, form an organ;
- Organ Systems: Multiple organs working together form organ systems that perform complex functions.
Aspects of Human Anatomy
| Aspect | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cells | Smallest units of life | Blood cells |
| Tissues | Group of cells performing a specific function | Muscle tissue |
| Organs | Tissues combined and functioning together | Heart |
| Organ Systems | Multiple organs working together | Cardiovascular system |
Importance of Human Anatomy
Human anatomy serves as a foundation for various fields such as medicine, physiotherapy, and even art. It provides the necessary information about the body’s structures, their locations, relationships with each other, and how they function. Here are some of the reasons why human anatomy is important:
- Medical Science: The knowledge of human anatomy is fundamental to diagnosing and treating diseases in medical science. It helps medical professionals understand where and how different structures in the body are likely to be affected by various medical conditions;
- Fitness & Physical Therapy: In fitness and physical therapy, understanding human anatomy is crucial for designing effective exercise programs and rehabilitation methods. It helps fitness professionals and physiotherapists to understand the workings of muscles, bones, and joints;
- Art: In the realm of art, human anatomy plays a pivotal role. Artists draw on their knowledge of the human form to create realistic and accurate depictions of the human body.
Human Anatomy and Art: An Inextricable Link
Art, specifically figure drawing and sculpture, draws heavily from human anatomy. The accurate portrayal of the human body in art is a testament to the artist’s understanding of the human form. This understanding not only enhances the visual appeal of the artwork but also instills a sense of life and reality into it.
The reasons why human anatomy is important to art include:
Realism
A solid understanding of human anatomy allows artists to portray the human body realistically, capturing the subtle nuances of different body parts and their proportions. Artists can depict the human form in various positions and from various angles with precision.
Expressiveness
Artistic works often aim to convey emotions and narratives. The knowledge of human anatomy aids artists in capturing these elements effectively by understanding how body posture, muscle tension, and facial expressions can communicate different emotions.
Creativity and Innovation
Understanding the ‘rules’ of human anatomy provides artists with the freedom to play with these rules, allowing for creative and innovative depictions of the human form. It can be seen in stylized art forms such as cartooning, caricature, and abstract art.
Sculpture
In sculpture, a 3D art form, the importance of human anatomy is magnified. Sculptors must understand how the human form looks from all angles to create lifelike pieces.
Understanding Anatomy for Artistic Expression
Artists use their understanding of human anatomy to translate their observations into artistic expressions. They study the human body in detail, understanding the bones that make the structure, the muscles that allow movement, and the skin that envelopes it all.
Aspects of Human Anatomy in Artistic Expression
| Aspect | Importance in Art |
|---|---|
| The Skeletal System | Provides the framework of the body, helps in depicting the body in various positions and movements |
| The Muscular System | Gives the body shape and enables movement, helps in capturing the dynamics of the human form |
| The Skin | Presents the visible outer surface of the body, helps in understanding how the skin wrinkles, stretches, and folds over the underlying structures |
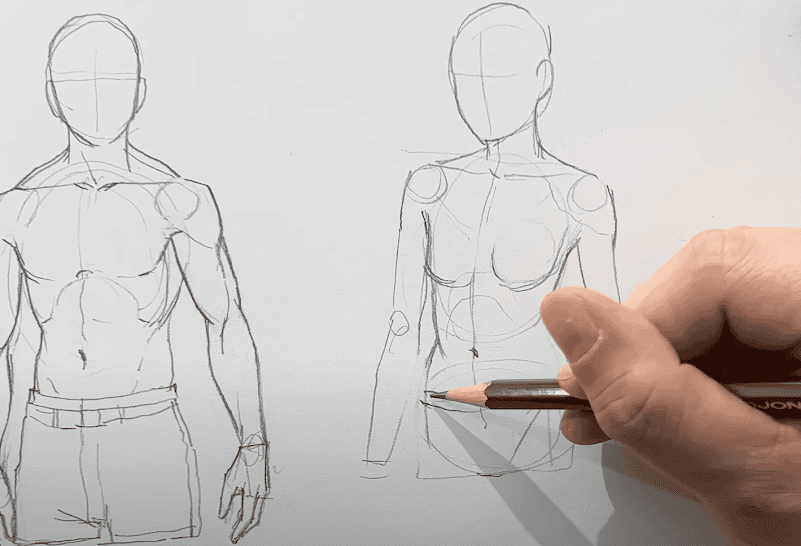
The Evolution of Anatomy in Art
The significance of human anatomy in art is not a new concept. Throughout history, the relationship between the two has continuously evolved.
- Ancient Times: Early depictions of the human form were more symbolic than realistic, focusing on the importance of figures rather than their anatomical accuracy;
- Classical Period: The Greeks and Romans paid attention to human anatomy, leading to more realistic and proportionate depictions of the human form;
- Renaissance: Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo studied anatomy in detail, leading to artworks that showcased a deep understanding of the human body;
- Modern and Contemporary Art: Artists began to experiment with form, leading to abstract and stylized depictions. However, even these works often relied on an understanding of anatomy for their foundation.
The Artistic Language of Anatomy
Artists, through their deep understanding of human anatomy, are able to speak a unique language. This language allows them to convey a multitude of narratives and emotions, all through the careful depiction of the human form. This artistic language of anatomy includes:
- Posture: The way a person stands or sits can tell a lot about their state of mind. Artists use this to their advantage to depict a variety of moods and emotions;
- Expression: Facial expressions are an integral part of human communication. Artists can convey a myriad of emotions through the careful rendering of facial features;
- Gesture: Hand and body gestures can add a dynamic element to art. They can suggest action, communicate emotion, and provide context to the artwork.
The Integration of Art and Anatomy in Education
Given the significant role human anatomy plays in art, it’s not surprising that many art education programs incorporate anatomy studies into their curriculum.
Integration of Art and Anatomy in Education
| Activity | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Life Drawing Classes | Students draw from live models to understand the human form in its most authentic state. These classes help students learn about proportions, movement, and the interplay of light and shadow on the human form. |
| Anatomical Studies | These studies involve a detailed exploration of the skeletal and muscular systems. They aid in understanding the underlying structure of the human body and how it influences the visible form. |
| Sculpture Classes | Sculpture allows for a 3D exploration of the human form. It enhances the understanding of how the human form appears from various angles. |
Tools for Studying Anatomy in Art
There are numerous resources available for artists who wish to deepen their understanding of human anatomy. These include:
- Anatomy Books: Comprehensive guides that provide detailed illustrations and explanations of the human body;
- Anatomical Models: 3D models that allow artists to study the human form from all angles;
- Online Resources: Websites and apps that offer interactive, digital anatomy tools for study and reference.
The Artistic Journey: From Anatomy to Creation
The journey of an artist from studying human anatomy to creating a piece of art is a meticulous and profound process. Here’s a simplified breakdown of this process:
Observation
Observation is a crucial step in the artistic process, allowing the artist to gather information and insights about the subject they are about to depict. This phase involves careful and attentive scrutiny of the subject’s form, posture, and expressions. By dedicating time to observing the subject, the artist can develop a deeper understanding of its unique characteristics, enabling them to effectively capture its essence in their artwork.
During the observation stage, the artist pays close attention to various aspects of the subject. They study:
- Form: Examining the subject’s physical appearance, proportions, and overall structure to recreate depth and volume on a two-dimensional canvas;
- Posture: Observing how the subject carries itself, the positioning of its body parts, and any distinctive gestures or movements to convey liveliness and dynamism;
- Expressions: Noting the subject’s facial expressions, muscle movements, wrinkles, and overall mood to accurately depict its emotional state.
Understanding Anatomy
Understanding anatomy is a fundamental aspect of an artist’s skill set, particularly when depicting the human form. By applying their knowledge of human anatomy, artists can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying structures of the subject they are portraying. This understanding allows them to accurately represent the form, proportions, and movements of the human body in their artwork.
When studying anatomy, artists focus on several key areas to enhance their understanding:
- Proportions and landmarks: Artists learn about the standard proportions and landmarks of the human body, such as the placement of the head, shoulders, torso, limbs, and major joints. This knowledge provides a foundation for creating well-proportioned and realistic figures;
- Surface anatomy: Artists observe the surface features of the body, including muscles, tendons, veins, and bony prominences. This attention to surface anatomy enables them to add realistic details and textures to their artwork, enhancing its visual impact and authenticity.
Sketching
Sketching is an essential technique employed by artists to bring their creative vision to life. It serves as a preliminary step in the artistic process, allowing the artist to develop and refine the basic form of their subject before adding more intricate details. When starting a sketch, artists typically follow a systematic approach, often beginning with the skeletal structure and progressively adding layers of muscles and skin.
The process of sketching involves the following stages:
- Skeletal structure: Artists start by sketching the underlying framework of the subject using basic shapes and lines. This step establishes the overall proportions and basic pose of the figure. By focusing on the skeletal structure, artists lay the foundation for accurately representing the body’s fundamental form and posture;
- Muscles: Once the skeletal framework is established, artists proceed to add muscles to their sketches. They consider the location and function of different muscle groups to depict the body’s contours and volume;
- Skin and surface details: After capturing the muscles, artists move on to adding the skin and surface details to their sketches. This step involves adding texture, wrinkles, folds, and other unique features that contribute to the subject’s appearance. Artists pay attention to light and shadow to create a sense of depth and three-dimensionality, enhancing the realism of their artwork.
Detailing
Detailing is a crucial stage in the artistic process where the artist adds intricate elements that bring the artwork to life. After capturing the basic form of the subject, artists shift their focus to adding specific details such as facial features, hair, and clothing. This stage involves careful observation, attention to proportions, and the utilization of various techniques to achieve realism and visual interest.
When it comes to detailing, artists typically follow a step-by-step approach:
- Facial features: Artists begin by adding facial features to the subject. They carefully observe the subject’s eyes, nose, mouth, and other distinctive characteristics. Proportions and symmetry play a vital role in accurately representing these features, as small deviations can significantly impact the likeness and overall expression of the subject;
- Hair: The next step involves adding hair to the subject. Artists consider the texture, length, and style of the hair, paying attention to its flow, volume, and individual strands. Techniques such as hatching, cross-hatching, or stippling are often employed to depict the hair realistically, capturing its unique qualities and creating depth;
- Clothing and accessories: Artists then focus on detailing the subject’s clothing and any accessories they may be wearing. This involves studying the fabric’s texture, folds, and patterns, as well as accurately representing the drape and fit of the garments. Artists may use shading, highlighting, or various brushwork techniques to convey the material’s characteristics and create a sense of realism.
Shading and Coloring
Shading and coloring are crucial techniques that artists employ to add depth, dimension, and a sense of realism to their artwork. These techniques enhance the visual impact and create a more lifelike representation of the subject. By skillfully manipulating light and color, artists can evoke mood, create texture, and bring their artwork to life.
The process of shading and coloring involves the following steps:
- Understanding light and shadow: Artists begin by studying how light interacts with different surfaces and objects. They analyze the direction, intensity, and quality of light sources to determine where shadows fall and how they affect the subject;
- Rendering shadows: Using various shading techniques such as cross-hatching, stippling, or blending, artists carefully apply shadows to their artwork. They consider the tonal values and gradations, gradually building up the darkness and intensity of the shadows to create depth and volume;
- Adding highlights and reflections: Artists then introduce highlights and reflections to the artwork. Highlights are areas where light directly hits the subject, creating bright spots and adding emphasis;
- Coloring and blending: Once the shading is established, artists proceed to add color to their artwork. They carefully select a palette that complements the subject and the overall mood they aim to convey. Artists employ various techniques such as layering, blending, and glazing to achieve smooth transitions, vibrant hues, and realistic color representation.
Conclusion
The study of human anatomy is an integral part of the artist’s toolkit. It enriches their understanding of the human form, enabling them to create art that resonates with viewers on a deeply human level. This rich intersection between science and art not only enhances the visual appeal of the artwork but also allows artists to tell compelling stories that captivate and engage their audience.